Table of Contents
Understanding the Essence of Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) has transcended its conventional definition as a mere gatekeeper to digital resources. In the current landscape, it stands as a pivotal component of organizational security and efficiency. IAM orchestrates the complex interplay between user identities, their authentication, and the access granted to resources. At its core, IAM is not just about allowing the right person access to the right data; it’s a meticulous framework ensuring security, compliance, and seamless user experiences.
The Significance of IAM in Modern Enterprises
In the ever-evolving digital ecosystem, IAM serves as the bedrock of an organization’s security posture. Its significance extends across multiple domains:
1. Enhanced Security Measures
IAM fortifies an organization’s defenses by ensuring that only authorized individuals gain access to sensitive data and resources. Advanced authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometrics, bolster this security shield.
2. Regulatory Compliance Assurance
With a labyrinth of data protection regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, IAM becomes indispensable. It aids in compliance adherence by meticulously managing access permissions and maintaining audit trails.
3. Heightened Operational Efficiency
Efficient IAM systems streamline access to resources, mitigating the risk of bottlenecks caused by unauthorized access attempts or administrative errors. This streamlined access fosters productivity and operational fluidity.
Components of IAM Systems
IAM systems comprise several fundamental components, each playing a critical role in safeguarding digital assets:
1. Authentication
Authentication methods validate and confirm the identity of users attempting to access the system or resources. These methods range from traditional passwords to more advanced biometric scans and smart cards.
2. Authorization
Authorization defines what resources authenticated users can access, based on predefined policies, roles, and permissions.
3. Administration
IAM administration encompasses user provisioning, de-provisioning, and ongoing management, ensuring that users have appropriate access throughout their lifecycle within the organization.
4. Identity Governance
Identity governance involves defining and enforcing policies and regulations that govern user access, ensuring compliance, and mitigating risks.
IAM Life Cycle
The IAM life cycle encompasses the various stages a user undergoes within an organization:
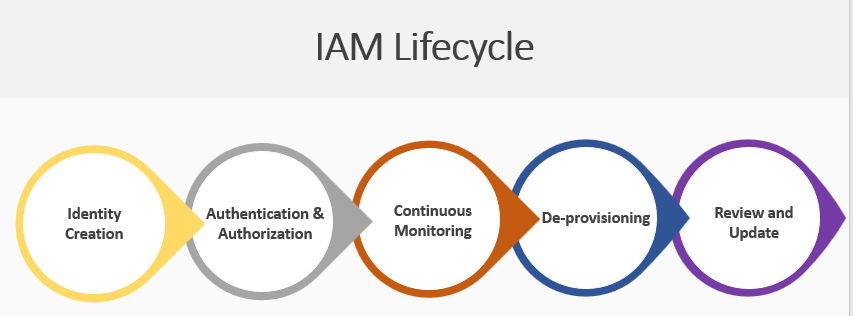
1. Identity Creation
This initial phase involves the creation of a user’s digital identity upon onboarding into the organization’s systems.
2. Authentication and Authorization
Once the user identity is established, the system verifies their authenticity and assigns appropriate access permissions.
3. Continuous Monitoring
IAM systems continuously monitor user activities, ensuring compliance with policies and regulations. Any anomalies or suspicious activities trigger alerts for further investigation.
4. De-provisioning
Upon employee offboarding or role changes, IAM systems ensure the removal or adjustment of access privileges to prevent unauthorized access.
5. Review and Update
Periodic reviews of access rights and policies ensure that the IAM system remains aligned with organizational changes and evolving security requirements.
Benefits of Implementing IAM Systems

1. Enhanced Security
IAM strengthens security by mitigating risks associated with unauthorized access and reducing the attack surface for potential breaches.
2. Improved User Experience
Efficient IAM systems streamline access, offering a seamless user experience while ensuring security protocols.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Meeting stringent compliance requirements becomes feasible through well-implemented IAM strategies, avoiding legal repercussions
Types of IAM (Identity and Access Management)
IAM solutions come in various types, each designed to address specific organizational needs and security requirements. Here are the key types of IAM:
1. Single Sign-On (SSO):
SSO enables users to access multiple applications or systems with a single set of login credentials. This streamlines user experience by eliminating the need for multiple passwords while enhancing security through centralized authentication.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification to access systems or data. It commonly involves a combination of something the user knows (password), something they have (token or device), or something they are (biometrics).
3. Privileged Access Management (PAM):
PAM focuses on managing and controlling privileged accounts, which have elevated access rights within an organization. It safeguards critical systems and sensitive data by strictly controlling and monitoring privileged access.
4. Identity Governance and Administration (IGA):
IGA solutions focus on governing and managing user identities and their access rights across the organization. They ensure compliance with regulations, manage user provisioning, and maintain a comprehensive view of user access.
5. Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM):
CIAM is specifically tailored for businesses that interact with external users, such as customers, partners, or vendors. It manages their identities and access to services, providing a seamless and secure experience for external users.
6. Adaptive Authentication:
Adaptive authentication systems dynamically adjust the level of authentication required based on contextual factors such as location, device, user behavior, and risk assessments. It provides a more flexible and risk-aware authentication process.
7. Cloud IAM:
Cloud IAM solutions are designed for managing identities and access control in cloud-based environments. They offer scalability, flexibility, and centralized control over user access to cloud services and resources.
8. IoT Identity Management:
With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, IoT Identity Management focuses on securely managing identities and access permissions for connected devices, ensuring their authentication and secure interactions.
9. Federated Identity Management:
Federated IAM allows users from different organizations or domains to access shared resources or services securely without the need for separate authentication. It forges trustworthy connections between identity providers and service providers, fostering a reliable framework for authentication and access.
10. Biometric Authentication:
This type of IAM uses unique biological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans for user authentication. Biometrics offer a high level of security and user convenience in authentication processes.
Implementing IAM: Best Practices
Implementing Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a critical process that requires careful planning, execution, and maintenance to ensure its effectiveness. Below are some best practices to consider when implementing IAM within an organization:
1. Comprehensive Assessment:
Before implementation, conduct a thorough assessment of existing systems, applications, and user access levels. Identify potential security gaps, user behavior patterns, and data sensitivity to create a solid foundation for IAM deployment.
2. Establish Clear Objectives:
Define clear objectives and goals for the IAM implementation. Determine what issues the IAM solution should address, whether it’s enhancing security, streamlining user access, or ensuring compliance with regulations.
3. Engage Stakeholders:
Involve key stakeholders across departments—IT, security, compliance, and business units—to gain insights into their specific requirements and concerns. Their input will help tailor the IAM solution to meet diverse organizational needs.
4. Adopt a Layered Security Approach:
Implement a layered security approach within IAM. Utilize multiple authentication factors, such as passwords, biometrics, tokens, and smart cards, to add layers of defense against unauthorized access attempts.
5. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
Implement Role-Based Access Control to assign access rights based on user roles. Define and manage permissions in a granular manner, ensuring users have access only to what’s necessary for their roles.
6. Regular Audits and Reviews:
Conduct regular audits and reviews of access controls, permissions, and user activities. This helps in identifying anomalies, enforcing compliance, and adjusting access rights as per organizational changes.
7. User Training and Awareness:
Provide comprehensive training and awareness programs to educate users about IAM policies, best practices, and the importance of security protocols. Encourage users to adopt secure behaviors and report suspicious activities.
8. Scalability and Flexibility:
Choose an IAM solution that can scale along with organizational growth and technological advancements. Ensure the solution remains flexible to accommodate new applications and evolving security requirements.
9. Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response:
Implement robust monitoring tools to continuously track user activities and system behavior. Establish a well-defined incident response plan to address security breaches or anomalies promptly.
10. Regular Updates and Maintenance:
Stay updated with the latest security patches, software updates, and IAM technology advancements. Regularly maintain and optimize the IAM infrastructure to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Implementing IAM involves a multifaceted approach that integrates technology, policies, and user behaviors. Following these best practices can significantly enhance the effectiveness and security of an IAM solution within an organization.
IAM: Q&A
Q1. What is the primary purpose of Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
A: IAM serves as a framework that manages and controls digital identities within an organization. Its primary goal is to ensure that the right individuals have access to the right resources at the right time.
Q2. How does IAM authenticate users?
A: IAM employs various authentication methods, such as:
Passwords: Traditional but still widely used.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requires multiple forms of verification, such as passwords, tokens, or biometrics.
Biometrics: Utilizes unique biological traits like fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans.
Single Sign-On (SSO): Allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of login credentials.
Q3. What role does IAM play in compliance and governance?
A: IAM ensures compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and others by:
Managing access permissions based on defined roles and policies.
Providing audit trails and detailed reports for compliance assessments.
Enforcing security protocols to safeguard sensitive data.
Q4. How does IAM handle user lifecycle management?
A: IAM systems manage the entire user lifecycle, including:
Provisioning: Creating user identities and granting initial access.
Authentication: Verifying user identities through authentication methods.
Authorization: Assigning access rights based on roles and permissions.
De-provisioning: Revoking access upon user offboarding or role changes.
Q5. What challenges exist in implementing IAM solutions?
A: Common challenges in implementing IAM include:
Complexity: Integrating IAM with existing systems and applications.
User Adoption: Encouraging users to adapt to new authentication methods.
Balancing Security and Usability: Ensuring stringent security measures without compromising user convenience.
Q6. Can IAM improve operational efficiency?
A: Yes, IAM enhances operational efficiency by:
Streamlining access to resources, reducing downtime due to access issues.
Automating user provisioning and de-provisioning processes.
Providing a unified view of user access across systems.
Q7. What is the future outlook for IAM technologies?
A: The future of IAM involves:
Zero Trust Security: Moving beyond perimeter-based security to validate every access request.
AI and ML Integration: Utilizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) for predictive analysis and threat detection.
Biometric Advancements: Continued enhancements in biometrics for more secure and user-friendly authentication.
Q8. What Are the Key Challenges in Implementing IAM Solutions?
A. Implementing IAM systems can pose challenges related to complexity in integration with existing systems, user resistance to new authentication methods, and ensuring a balance between security and user convenience.
Q9. How Does IAM Impact User Experience?
A. A well-designed IAM system offers a seamless and secure user experience by providing quick and secure access to resources without compromising on security measures.
Q10. What Role Does IAM Play in Regulatory Compliance?
A. IAM systems assist organizations in complying with stringent data protection regulations by meticulously managing access controls, ensuring data privacy, and maintaining audit trails.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Identity and Access Management stands as a linchpin in securing organizational assets, ensuring compliance, and fostering operational efficiency.
Its holistic approach to managing user identities and their access rights makes it a crucial aspect of modern digital enterprises.
You can follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter for IT updates.
Also read..
Top 10 Active Directory Attacks Methods

